What is “Footballers Groin”?
By Sports Physio, Greg Wootton
Groin pain is commonly reported by young sports participants, particularly young males that play kicking sports.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Footballers Groin?
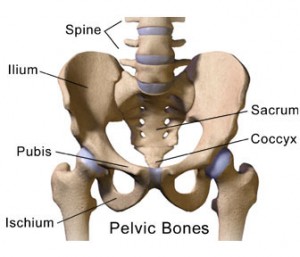
An athlete with Footballers Groin will typically report pain, tightness and tenderness in the inner thigh; and central tenderness and pain local to the pubic symphysis (this is the bony joint low down in the middle of your abdomen, just above our genitals)
Some report a deep ache in the genital area and the lower abdomen. Symptoms are usually associated with the kicking, jumping, sprinting and twisting activities of some sports and these stop/start, change of direction or single leg activities will cause aggravation. If the pain becomes worse, it may even be present just to walk around.
So what IS Footballers Groin?
Pain in the Groin region may be due to a multitude of conditions including hip joint pathologies, bursitis (irritation of the sack of fluid that usually sit below a tendon and stops the tendon rubbing directly on the bone) of the psoas muscle (one of the hip flexor muscels), stress fractures in the pelvis or hip, avulsion fracture (a bone fracture where the muscle contracts so strongly that it fractures off a portion of bone) , nerve compression and low back pathologies. These conditions all make diagnosis of the reason for Groin Pain very complex.
The term “Footballers Groin” was coined to refer to multiple conditions of the pelvis and lower limb that regularly affect sportspeople participating in sports involving a kicking action. The diagnosis includes a combination of osteitis pubis (discussed below), adductor tendonopathy (damage to the adductor, or groin muscles as they attach in to the pelvis bone) and a sports hernia.
Some individuals may also have abdominal muscle pathology where these muscles insert into bone around the pubic symphysis (and a section of abdominal tendon called the conjoined tendon).
Osteitis pubis involves inflammation/irritation of the pubic symphysis , the joint at the front of the pelvis between the two pubic bones. As the inflammation and irritation continues bone marrow oedema (bone stress) and bony degenerative change occurs.
Adductor insertional tendonopathy is micro and macro trauma of the tendon associated with activity, resulting in structural changes in the tendon, similar to a variety of overuse type tendonopathies such as tennis elbow or the Achilles.
The term “sports hernia” refers to a deficiency of the wall of the inguinal canal, although unlike other many other hernias, it typically does not have a palpable lump or protrusion.
The irritation in Footballers Groin is thought to be a product of shear forces on the pubic bones of the symphysis pubis joint due to weight bearing on a single limb. These forces are then multiplied with kicking, jumping or changes of direction whilst under load. If these forces cannot be adequately controlled the movement at the symhysis pubis irritates and degenerates the bony surfaces. In an attempt to control the shear forces the athlete may overload the adductor and abdominal muscles.
What is the Cause?
A lack of the muscle control and stabilisation of the pelvis is considered the primary cause of Footballers Groin.
Specifically, poor functioning of the gluteal and deep pelvic muscles responsible for stabilising the pelvis and reducing shear forces through the pelvis. A direct link has been shown between decreased function of the gluteus medius and subsequent over activity of the adductor longus muscle.
Decreased hip joint mobility has also been shown to increase loading on the pelvic structures.
What does Treatment Involve?
A myriad of factors must be considered in the treatment and rehabilitation of the “Footballers Groin”. Initially the reduction of aggravating activity to reduce inflammation and degenerative changes may reduce symptoms, but if muscle control of the pelvis and lower limbs is not corrected it is likely symptoms will return with a return to activity.
Exercises to improve dynamic (movement) stabilisation of the pelvis should be commenced and gradually the loads and dynamic components of the exercises increased. The exercises are then advanced to include sport specific training in preparation for a return to the field.
All the Physio’s at GCPSH are able to help Manage you, or your child, if experiencing Groin Pain. In particular, Sports Physio Greg Wootton worked with a WA AFL football team for many years so has extensive experience in treating difficult groin pain and is happy to help any client at any level of competition.